Building Experience APIs
WaveMaker’s Java Integration Services let you extend and enhance your APIs —whether they come from database services, REST services, or other generated backend services. By using dependency injection, you can access these services directly in your Java code and orchestrate multiple backend sources into a single, unified API.
This enables you to build custom Experience APIs (BFF-style) that aggregate, transform, and expose data exactly the way your frontend requires, while also reusing WaveMaker-generated services and implementing advanced business logic.
Accessing Services from a Java Service
In WaveMaker, a Java Service acts as an orchestration layer that sits on top of existing backend services.
Database services, security services, and other generated services can be injected into a Java Service and reused as building blocks.
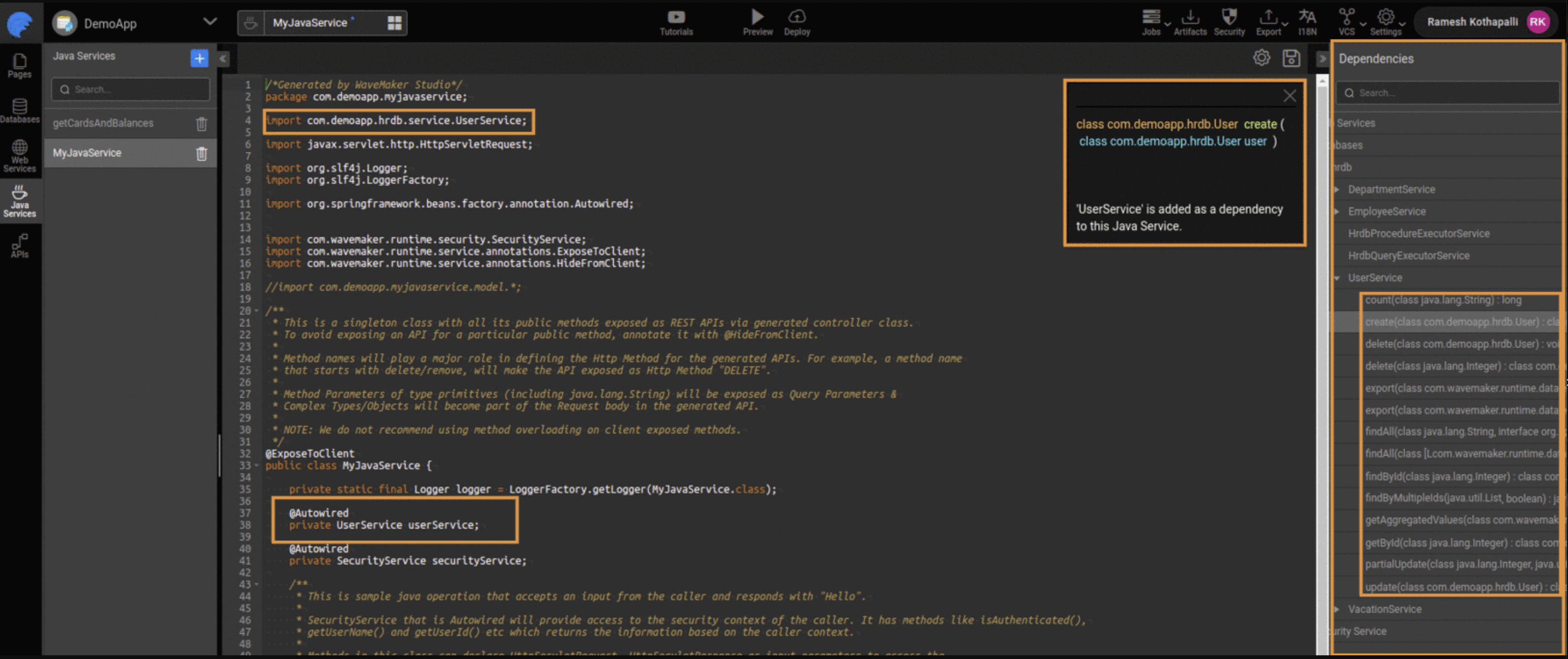
Once a service is added from the Dependencies panel, WaveMaker automatically wires it into the Java Service. This allows the Java Service to directly invoke database operations such as create, retrieve, update, and delete, without writing low-level persistence code.
The Java Service then coordinates these calls—fetching data from one service, enriching it with logic or context, and optionally combining it with data from other services—before returning a single, composed response to the client.
This flow enables Java Services to function as Experience APIs (BFFs), where backend complexity is hidden and the UI interacts with a simple, purpose-built API.
Example: Building Experience APIs Using Java Services
This example demonstrates how WaveMaker Java Services can be used to build Experience APIs (also known as Backend for Frontend – BFF). An Experience API orchestrates multiple backend services and exposes a single, UI-friendly endpoint tailored to application needs.
In this example, we demonstrate the following core concepts:
-
Service Orchestration
Combines multiple backend services (database and security services) into one API response. -
Dependency Injection
Uses Spring’s@Autowiredto inject and reuse existing services. -
Transaction Management
Applies a database-specific transaction manager to ensure consistency across operations. -
Security Context Access
Retrieves logged-in user information using WaveMaker’sSecurityService.
package com.wavemaker.myapp.userservice;
import com.wavemaker.myapp.hrdb.Employee;
import com.wavemaker.myapp.hrdb.Department;
import com.wavemaker.myapp.hrdb.service.EmployeeService;
import com.wavemaker.myapp.hrdb.service.DepartmentService;
import com.wavemaker.runtime.security.SecurityService;
import com.wavemaker.runtime.service.annotations.ExposeToClient;
import jakarta.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
@ExposeToClient
public class UserService {
@Autowired
private SecurityService securityService;
@Autowired
private EmployeeService employeeService;
@Autowired
private DepartmentService departmentService;
@Transactional(value = "hrdbTransactionManager")
public Map<String, Object> getEmployeeDashboard(HttpServletRequest request) {
Map<String, Object> response = new HashMap<>();
// Logged-in user
String userId = securityService.getUserId();
response.put("userId", userId);
// Employee details
Employee employee = employeeService.findById(Integer.valueOf(userId));
response.put("employee", employee);
// Department details
Department department = employee != null
? departmentService.findById(employee.getDeptId())
: null;
response.put("department", department);
return response;
}
}
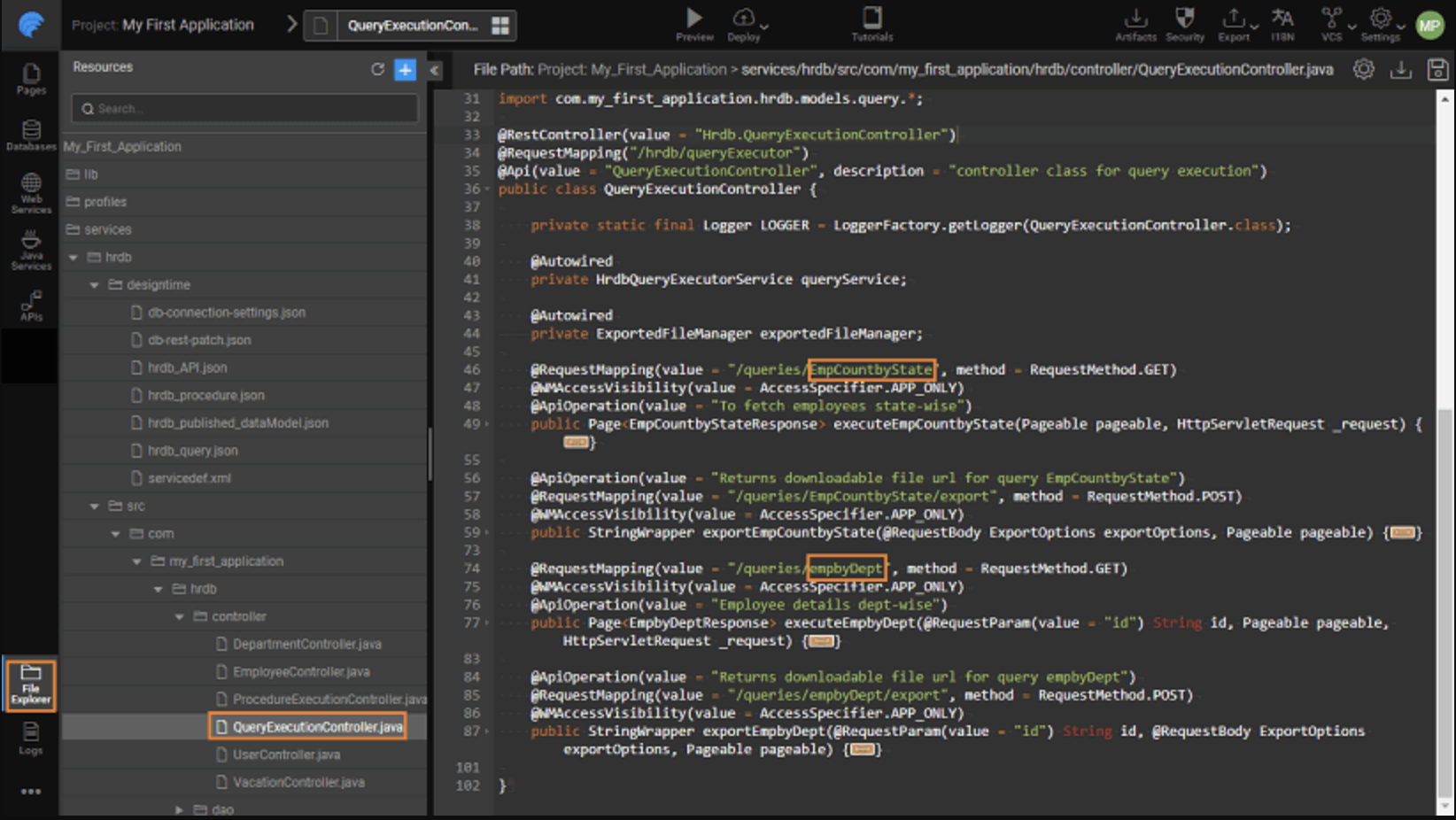
Accessing Named Queries
WaveMaker supports named queries defined in the database query editor. For each named query, WaveMaker generates a corresponding REST API and makes it available under the API Designer panel. These can be invoked using Java Services just like other database operations.
Integrating External Libraries
You can use third-party Java libraries within your Java Services in one of two ways:
Export the project to an IDE
Export your WaveMaker project to an IDE (e.g., Eclipse, IntelliJ), add external libraries, and then re-import it back into WaveMaker. Since the project uses Maven, dependencies are handled automatically. Synchronizing Wavemaker apps with IDE
Import JAR files into the project
Add external JARs as project resources and reference them in your Java Service code. Import Resource
This allows you to tap into capabilities beyond what WaveMaker provides out-of-the-box.
Summary
Java Integration Services enable you to:
- Reuse generated services (e.g., database, security, feed, and SOAP services) inside custom Java logic.
- Use Spring's dependency injection (
@Autowired) to access service beans. - Integrate external Java libraries and tools into your service layer.
This approach empowers you to extend backend logic while maintaining reuse and coherence with WaveMaker's service ecosystem.
How-To Guides
Learn more about working with Java services through these practical guides:
- Sending Email Using Java Service - Implement email functionality in your applications
- Implementing Forgot Password Feature Using Java Service - Build password recovery workflows
- Scheduling Java Service - Configure scheduled tasks and cron jobs
- Synchronizing Java Services with Controller - Coordinate service and controller layers
- Integrating Amazon Cognito for User Authentication - Add AWS Cognito authentication
- Accessing Logged-In User Information - Retrieve current user details
- Camunda and WaveMaker Integration - Integrate workflow management
- Accessing REST APIs from Java Service - Call external REST APIs from Java code
- Pre and Post Processing for Database Service APIs - Add hooks to database operations
- Custom Status Code and Error Messages - Handle errors and HTTP responses